 Reading Time: 8 minutes
Reading Time: 8 minutesThis is search engine optimization tip number fourteen in our continuing series of tips from search engine optimization company Vizion Interactive. All of our search engine optimization tips are very specific, should not take a long time to fix (or to check to see if you are following the search engine optimization best practices), and will be rather “short and sweet” and directly to the point.
Contents
If you have not been following along with all of our search engine optimization tips, you might want to take a look at some of the previous SEO tips that we have already talked about. The last SEO tip was about removing unused meta tags from your site. Then, for our search engine optimization tip number 12, I talked about the text surrounding your links. Then, in SEO Tip number 11, I talked about using keywords in your heading tags. These are important because using a H1 tag will give more “weight” to the heading and the keyword phrase you’re targeting on that page. In the SEO tip before that, search engine optimization tip number ten, we talked about checking your links on your site to make sure you are not linking out to any bad neighborhoods or other sites that you do not wish to continue to link to. In SEO tip number nine, we talked about linking out to web sites. In search engine optimization tip number eight, we talked about Alt Tags and how you need to make sure that your keywords are in your Alt Tags and that they need to describe specifically what the image is and what someone will see when they look at it. Previously, before that, we talked about the anchor text of internal links. Then, before that, we talked about having keyword in your urls, linking to your home page, the meta keywords tag, the keywords on your web page, the meta description tag, and your web page’s title tag. All of these “search engine optimization tips” are things I look at when analyzing a site or optimizing it for the search engines. Keep in mind, though, that this is only the beginning. There are a lot more search engine optimization tips coming.
For search engine optimization tip number fourteen, let’s talk about fixing duplicate content on your web site. The search engines, mainly Google, do not want to index duplicate web pages on your web site: it takes up room in their database and slows down their indexing and crawling. Furthermore, it ultimately makes our search experience better. Let’s take a look at an example of what a search engine results page would look like if all we got were duplicate web pages when we searched?
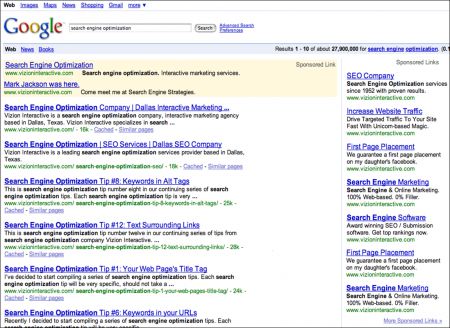
Why Do Search Engine Care about Duplicate Content?
There really are a lot of reasons why a search engine would care about duplicate content. Removing duplicate pages allows search engine to focus on indexing the “better” web pages. Search engine spammers create “millions” of useless web pages, filling up the search engines’ databases. The better quality search results they deliver, the more that you will want to use their search engine.
Identifying Duplicate Content, Google Patents and Papers
What really is duplicate content? In your mind? In Search Engines’ minds? Google takes a scientific approach to finding duplicate content. Google looks for main “identifiers” to “tip them off” to “dig deeper” to look for web pages that are duplicates. We don’t know exactly how Google does, it but based on published papers, Google first finds similar URLs, as well as similar (or the same) title tags of web pages. Once they find those, they then use other methods of checking and comparing web pages that they know about. There are a few resources to learn more about how Google finds and identifies duplicate content, including:
Google process for detecting near duplicate content
Stanford Paper: Detecting duplicates for web crawling
There are also some Google patents that talk about duplicate content. To find them, search Google for the title(s) of these patents:
- Google Patents regarding Duplicate Content
- Methods and apparatus for estimating similarity
- Detecting duplicate and near-duplicate files
Finding Duplicate Content on Your Web Site
The first thing you need to do is to identify if your web site contains duplicate content. There are several ways to do this, including searching for it. Use your favorite search engine (or MSN, Google, and Yahoo!) for the duplicate content. At Google, try using the site:domain.com command, where ‘domain.com’ is your domain name, like this:
site:domain.com
If you look at the search results, you should see unique title tags. If you see any pages that have the same title tag, you should be able to see them in the search results. Look at the number of pages Google has indexed. Look at the number of pages Yahoo! and MSN have indexed. The number of web pages indexed will vary from search engine to search engine, but if there is a big difference between any of the search engines you might want to investigate further. Google will typically show fewer pages indexed: Google tends to remove duplicate pages that they find. Take a look at Google’s Webmaster Tools; Yahoo! also has a similar service that might give you more information about your site.
Here are some other things you can do:
– Look for mirror web sites. How many domain names do you own? Do all of the domain names that you own redirect with a 301 Permanent Redirect to your main web site? EVen though it’s not necessarily related to finding duplicate content, I suggest that you make and keep up with a list of all the domain names that you have and their expiration dates.
– Look for similar title tags, similar meta description tags, similar meta keyword tags (as previously mentioned, Google Webmaster Tools and Yahoo! Site Explorer provides some great information if you verify your site with them.)
– Look for web pages on your site that are “light on indexable content”. In other words, you may have web pages that don’t have a lot of text on them: if two web pages don’t have much text on them (usually at least a few paragraphs of unique text) then there’s a chance that they might be considered to be duplicate web pages.
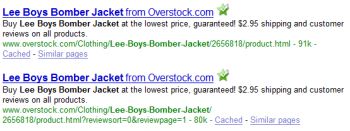
For example, ecommerce web sites that have short product descriptions typically tend to be considered duplicate web pages. The pages tend to be considered duplicates even if they “technically” have a different product photo or are a different color, size, or other features. The search engines compare one web page (as a whole) to another web page (as a whole). What do you need to do? Add more text to product descriptions. Hire a writer to write more content if needed.
- Look for “print versions” of an article or page, or “email to a friend” web pages on your site. These are typically duplicate web pages. What do you need to do? Use the robots.txt file, as well as a noindex meta tag on the page(s) to disallow indexing of one version of the web page.
- Canonicalization can also be something to fix. You need to choose one version of your web site, either www.domain.com or domain.com. These can lead to duplicate versions of your web site. Once you choose one, set up a 301 Permanent Redirect from one version to the other.
- Look for Session IDs (multiple URLs for the same content). You may need to remove the session IDs and other variables in your site’s URLs. You can rewrite the URLs or you can remove Session IDs.
- Watch out for blog archives, other templates, and themes (such as WordPress themses) that create multiple copies of your content. WordPress in particular is notorious for creating all sorts of duplicate content on web sites. What do you need to do? Use the Robots.txt file, and/or the noindex tag to disallow the content from getting indexed. I actually prefer to remove the internal links on the WordPress theme itself. If there are no links to the archives, then a search engine typically cannot find those duplicate web pages.
- If you find a domain name that is causing duplicate content:
- What do you need to do? Redirect the domain name(s) with a 301 Permanent Redirect to your main domain name.
- If the duplicate content is on your web site:
- What do you need to do? Disallow the duplicate content using the robots.txt file. You can also delete or redirect (with a 301 redirect) the content.
- If it’s “acceptable” content (e.g., print version, etc.):
- What do you need to do? Use the robots.txt file and the noindex meta tag to tell search engine spiders to ignore the content.
- If the duplicate content is not on your web site:
- Figure out if is really hurting your business and yoru web site’s search engine rankings. Are you ranking first for that content? Search for the title tag or a sentence on the page in quotes to see where your web page shows up in the search results. You should be first if you’re the originator of the content. If not (and you’re the originator of the content), then consider getting the content removed.
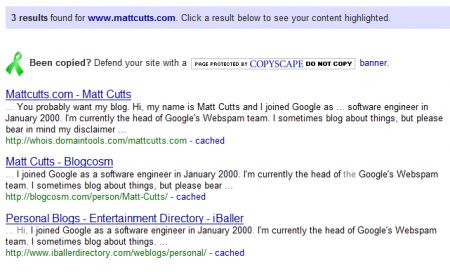
Is Someone Copying Your Content?
What do you do if someone copies your web site’s content? Or even just a part of it? There are several things you can do:
– Search for your content. Search for a sentence on your site using quotes (as previously noted).
– Set up Google and Yahoo! Alerts for a phrase on your web site. If someone copies your content in the future, you’ll be notified by Google or Yahoo! so you can deal with it.
– If you hire a writer to write content for you, make sure you use the Copyscape.com service to make sure it’s unique content.
We recently checked Copyscape for Matt Cutts and found a few web pages that are copying the content from his blog. Check your own web site and your web pages to see what you can find.
If Someone is Copying Your Content…
What do you do if you find someone has copied your web site content? First, calm down: it’s not that bad. There are things you can do:
Determine if the copied content is actually hurting your business. In many some cases, a syndication of your blog or use of your content is acceptable. If you are getting credit for the content (does it link back to your web site?), then it should be okay. Was your content indexed on your site first? If you rank first for the title of the page (in quotes) then it should be okay. Ultimately, you need to decided if it’s “worth your time” to get the content removed from someone else’s web site.
First, I recommend contacting the site owner to ask them to remove the content. If they don’t respond or are not nice about it, then consider filing a DMCA request to get the content removed from the other person’s web site. File the DMCA request with their web host and the search engines:
If you need a template for the letter you need to send, there are some DMCA Templates available.
Preventative Measures to Protect Content
There are several things you can do as “preventative measures” to protect your web site’s content. First, you’ll want to file a copyright with the US Government if you are located in the United States. There are other places to file if you are in another country.
- File the necessary paperwork (online or in writing) with the US Copyright office. See www.copyright.gov. The current fee is $35 for an online application.
- Consider hiring a writer to add additional content to your web site. If hiring a writer, always check the content with copyscape.com. You will probably need to put the content on the web temporarily to run it through copyscape.com.
- Always try to get your content indexed and crawled first. Consider adding links to new web pages on your web site’s home page. You might even add a section on your home page that highlights and links to the new content. The point is to get it crawled; it doesn’t have to be on the page permanently, just a few days; enough to get crawled. Then it can be added into the rest of the web site’s navigation. Consider submitting the content to the social media sites to force a crawl of the content.
Don’t be afraid to hire a writer to write unique content. Too many people just think it’s “easier” to copy someone else’s content. If you copy someone’s web site content, it will ultimately cost you more in the long run.
What’s the bottom line?
Duplicate content can hurt your web site’s search engine rankings. Google typically removes web pages from their index that they suspect are duplicate web pages. First, you need to identify the duplicate content on your web site. Remove, redirect, or use a noindex meta tag to tell the search engines to ignore it. Then, deal with copycats efficiently and effectively. In other words, don’t be lazy.
Additional Resources
Google has recently written a great post about “demystifying” the duplicate penalty.
At Vizion Interactive, we have the expertise, experience, and enthusiasm to get results and keep clients happy! Learn more about how our SEO Audits, Local Listing Management, Website Redesign Consulting, and B2B digital marketing services can increase sales and boost your ROI. But don’t just take our word for it, check out what our clients have to say, along with our case studies.




